When freezing temperatures permeate the air outdoors, a warm and comfortable home becomes a welcome reprieve. Over the centuries of experiencing the discomforts brought about by cold seasons, people have been continuously improving and redesigning heating systems for residential use. Because of this, today’s home heating systems come in a wide variety of designs. In other words, there are different heating systems made to meet every person’s needs.
Heating systems are appliances used for keeping comfortable temperatures stable. Usually, they come in two main types: central heating and direct heating. Using radiation, conduction, or convection, they can generate heat throughout the room or building.
Different types of heaters make use of different heating elements, which are usually made of nichrome. In addition to this, most modern heaters come with thermostats, which allow users to control the temperature.
With all the technological advancements in the heating industry, the number of heating solutions seems pretty overwhelming. It’s no surprise that most people find it challenging to choose the right heater. The best solution to this is to learn all of the common types of heaters. With this knowledge, you can easily make an informed decision when buying a heating system for your home.
Central Heating Systems
Central heating systems are mostly found in cold climates. The reason behind this is that central heating systems can generate warmth throughout a huge portion of a building, if not the entire building. When this system is combined with other systems to control the temperature, it can be considered an HVAC system.
Central heating systems are normally located in one room, like a mechanical room or a furnace room. From there, the central heating system generates heat to multiple rooms through ductwork or pipes. Because of this, central heating systems can also be found in commercial buildings, such as hotels, shopping malls, offices, and high-rise residential buildings. They also come in different types, but the most common ones are furnaces, boilers, and heat pumps.
1. Furnaces
The most common type of central heating system found in a majority of households in the U.S. is a furnace. By blowing heated air through a duct system, it can deliver warm air to multiple rooms. Oftentimes, furnaces are called forced-air heating systems. They can be powered by various types of fuel, but they usually run on oil, natural gas, and electricity.
Furnaces are not as expensive as other heating systems, and they are generally energy-efficient. However, their overall efficiency can likely degrade in the long run. The cost of running a furnace can vary according to electricity prices, fuel rates, or the cost of its source of energy. Furthermore, it requires a duct system on which it can be installed, and it can be potentially hazardous if gas leaks out of it. In spite of this, furnaces are widely available and easy to use. Also, they don’t need frequent maintenance. Furnaces are thus perfectly suitable for any kind of home.
2. Boilers
Mostly confused with furnaces, boilers are closed vessels designed for heating water. Unlike the forced air heat distribution system of furnaces, boilers distribute heat by letting the heated water pass through devices. These devices can be radiators, aluminum panels, or baseboard heaters. Afterward, the cooled water goes back to the boiler to be heated again.
A common misconception about boilers is that they boil water. While they don’t necessarily boil water, they increase its temperature to a comfortable level for various applications. Boilers are used not only for central heating but also for water heating, cooking, sanitation, and power generation.
Since boilers produce heat via hot water or steam, this type of heat is non-allergenic. Boilers are also energy-efficient, but they tend to be expensive to install since they make use of copper pipes. Moreover, the building must be kept at a minimum temperature to prevent the pipes of the boilers from freezing.
3. Heat Pumps
Heat pumps have become popular heating solutions among homeowners. With the use of refrigerants or other mechanical means, heat pumps can extract heat from outside sources, such as the air or the ground. Then, with the use of heat exchangers, they transfer the heat toward the interior of the building. This process can also be reversed, and it involves transferring heat from indoors to outdoors. This means that heat pumps can be used for cooling too, particularly during hotter months. For this reason, heat pumps are found in many HVAC systems and regarded as two-way air conditioning units.
The heat pump is the most energy-efficient among the three common types of central heating systems. It can operate throughout the year for heating and cooling purposes while saving more energy than other systems. However, heat pumps can be inefficient in colder climates with an ambient temperature of below 32 degrees Fahrenheit, so they are better suited in moderate climates. Also, installing heat pumps tends to be quite expensive.
Direct Heating Systems
Central heating systems can generate heat for multiple rooms, whereas direct heating systems are commonly used for providing one room with supplemental heat. While this fact rings true for most direct heating systems, some of them are designed to warm up several rooms. Other direct heating systems can also be installed on pre-existing central heating systems.
1. Space Heaters
When one room of the building isn’t heated by the central heating system, putting a space heater in place is your best solution. Space heaters can produce supplemental heat throughout a single room, and they conveniently contain heating, distribution, and regulation systems. Most of these heaters are powered by gas or electricity.
A. Gas Space Heater
Space heaters that run on natural gas, kerosene, or propane are popular heating solutions in unheated areas, like daylight basements or garages. Gas heaters are less expensive to run than electric space heaters. They can also quickly provide heat throughout the room. The downside of using gas heaters is that they pose a risk of carbon monoxide leaking into the room. That’s why they need to be installed with a vent, making them more complicated to install than other heating systems.
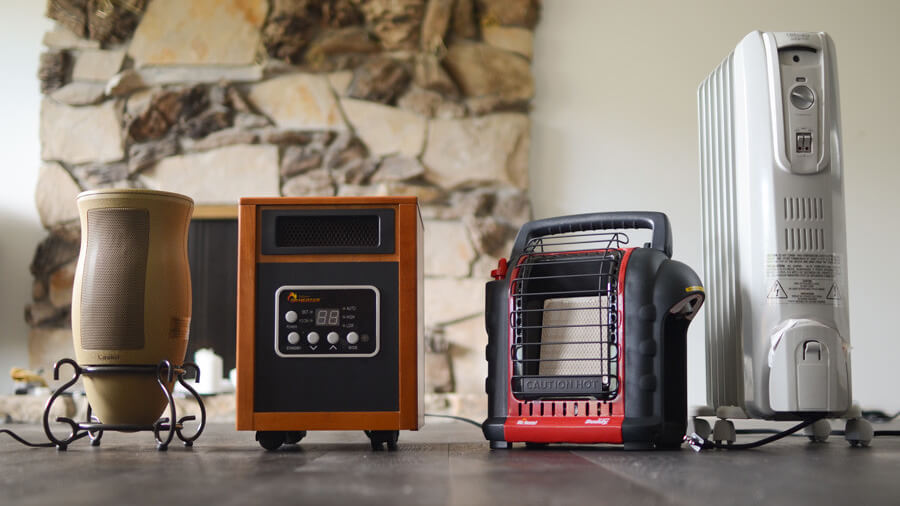

B. Electric Space Heater
Electric space heaters are the simplest heating solutions as they are sold at relatively low prices in most stores. They come in a variety of styles, and they usually have several safety features in place. Simply plug an electric space heater into a power outlet, and it can quickly convert electric current into heat.
In spite of their convenience and ease of use, they can consume a considerable amount of electricity just to produce the same amount of heat that gas space heaters can generate. Because of this, regular use of electric space heaters can cause your electricity bills to skyrocket.
2. Electric Baseboard Heaters
Electric baseboard heaters can operate quietly, and they do not require much maintenance. Using convection, these heaters deliver hot air out of their top slots while drawing cool air into their bottom slots. With this feature, they can provide the room with even warmth without consuming a huge amount of electricity. They are also best installed under windows and right above the floor. This way, they can eliminate cold drafts and prevent heat loss at the same time.
Since baseboard heaters can spread heat evenly and efficiently, they are perfect for drafty areas that are difficult to warm up. For optimal heating performance, they need to be unobstructed by curtains, drapes, or furniture.
3. Kickbases
Also known as kick-space heaters or toe-kick heaters, kickbases are ideal solutions for uncomfortably cold rooms. Their name originates from the fact that they are designed to be installed in the cavities beneath cabinets or bathroom vanities. The compact sizes of these heaters allow them to fit perfectly in narrow spaces. As they generate supplemental heat, they can stay well-hidden from view and seamlessly blend in chilly rooms.
4. Cove Heaters
Arguably the most stylish type of heater, a cove heater is named as such since it was originally designed to be installed on the cove. Today, cove heaters are often mounted on the wall right below the ceiling, so they do not take up any floor space.
What’s great about cove heaters is that they use radiant heat, which means that they warm up nearby objects instead of the air. Since they generate radiant heat, they can be installed virtually anywhere. With a cove heater, you can have comfortable warmth without having a bulky appliance in your way.
Some cove heaters feature concave surfaces and sawtooth profiles, and this design is not just for aesthetic purposes. This sleek, clever design enables the heat to travel around the room and toward its center. For this reason, this type of heater can raise the room’s temperature quickly and allow quick recovery from heat loss.
5. Convection Heaters
Convection heaters produce warmth with the use of convection. Basically, convection refers to the transfer of heat caused by the tendency of hotter, less dense air to rise and colder, denser air to sink. Using this principle, a convection heater warms up the air and allows it to rise. As the air cools down, it reheats the air over a heated coil, and the heated air naturally rises again. Thus, a convection heater can spread out warmth uniformly across any room without consuming too much energy.
Convection heaters come in different designs, such as wall-mounted, freestanding, and floor-recessed. Some of these heaters come with fans to force out the heated air. Other convection heaters don’t need to make use of fans, so they operate more quietly.
6. Radiant Heaters
Radiant heaters can be installed on the ceiling, floor, and walls, which is why they don’t take up too much space in rooms. Unlike other types of heaters that transfer heat by air, radiant heaters directly warm up objects and people that are close by. Because of this, they neither distribute allergens nor change the flow and content of the air, making them suitable for allergy sufferers. Radiant heaters also produce heat at a set temperature without the need to push it toward the ceiling, which means that they are pretty energy-efficient.
7. Infrared Heaters
Like the natural heat coming from the sun, infrared heaters emit healthy and comfortable warmth, which is then absorbed by the skin. While some heaters can cause dry air and static electricity, infrared heaters do not alter the humidity and oxygen levels in the room. Since they directly transfer heat instead of warming up the air, they can heat the room in no time. As long as infrared heaters are used, there won’t be any loss of heat or energy.
With infrared heaters, you can enjoy the comfortable sun-like warmth without suffering from the harmful effects of ultraviolet rays. Another great thing about infrared heaters is that they operate noiselessly and require minimal maintenance.
8. Pellet Stoves
Using compressed wood or pellet fuels, pellet stoves offer efficient heating without emitting high amounts of toxic fumes. Before, wood burning in wood stoves has caused a huge problem of pollution in the U.S. Today, however, there are new models of pellet stoves that are designed for clean-burning.
Compared to wood stoves, pellet stoves are easier to install, produce less smoke, and cost less. The problem with these stoves is that they tend to operate with noise and require regular maintenance. Most pellet stoves also require electricity to operate. Moreover, if the supply of pellet fuels is not readily available in your area, then running a pellet stove can get expensive.
Choosing the Best Heater for Your Home

There are several things to consider when choosing the right heater for your home. As with all buying decisions, the first thing to factor in is your budget. This does not only mean the price of the heating system you plan to buy. It also means the cost of operating it. Furnaces and heat pumps are the go-to heating systems of most homeowners since they are highly efficient in heating the whole house.
You should also consider which rooms in the house you need to heat and how large these rooms are. Electric baseboard heaters are suitable for drafty rooms, while radiant cove heaters can quickly provide comfortable heat throughout any room. For small rooms, ceiling heaters and wall heaters are perfect as they won’t take up any floor space. There are also specialty heaters designed for specific rooms or areas in the house, such as kickbases for bathrooms and pump house heaters for sheds and utility closets.
It’s also best to take advantage of existing duct systems in your house by simply installing duct heaters. This way, you don’t have to purchase expensive heating systems, and you can have a central home heating system in a flash.
Lastly, buying heating systems from well-established HVAC manufacturers is definitely a wise investment decision. By doing so, you won’t have to worry about substandard and easily breakable heaters. Engineer Warehouse understands how important a heating system is in any home. That’s why we offer top-of-the-line heaters of the best HVAC brands. With these highly efficient heaters, you can have a comfortable and toasty home all year round.